Drone applications are transforming industrial operations worldwide by offering fast, efficient, and innovative methods of collecting and delivering data. These flying gadgets, known as ‘Unmanned Aerial Vehicles’ (UAVs), are being widely adopted across various industries for their versatility and effectiveness.
UAVs come in different sizes and types, each designed for specific tasks, making them valuable tools in sectors like agriculture, film production, surveying, logistics, and more. Drones improve safety, speed, and accuracy in work processes, enabling industries to operate more efficiently and effectively.
In this blog, we explore the various drone applications across major industries. You’ll discover where and why drone applications are making the most significant impact.
The Application of Drones and How They Work?
Drones are innovative flying machines that perform tasks with utmost precision across various applications in almost any industry. They cannot operate without a human pilot and offer flexibility and accuracy.
As drone technology advances, these flying objects become more innovative and commonplace in almost every industry. A good understanding of the applications of drones helps a user maximize their value.
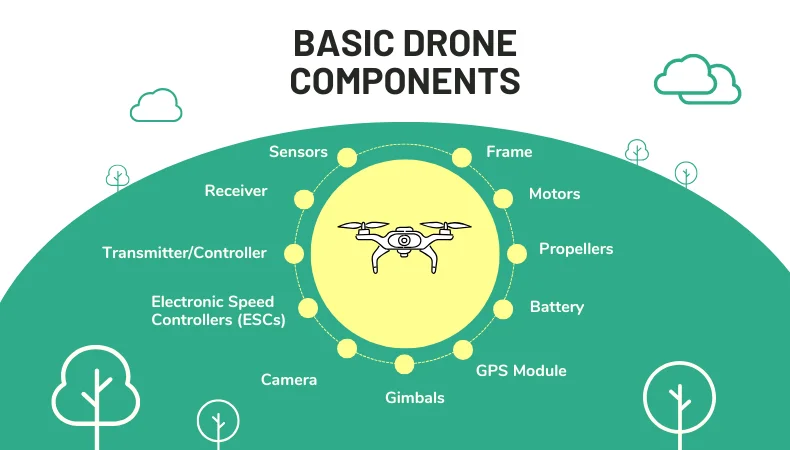
Propellers
Drone propellers are primarily responsible for the application of lifting the drone while controlling its movement in the air. Their speed and direction help maintain the drone’s stability during its flight.Cameras and Sensors
Drones frequently mount high-resolution cameras to capture close-up images or videos. Advanced sensors enable remote sensing for mapping, monitoring, or inspection. Such capabilities allow drones to survey areas that are hard to reach safely.The Application of Drones in GPS Systems
Drone application of GPS offers positional information to help it pursue its flight paths and return to its home, often following alternative trajectories. It allows the drone to conduct accurate navigation in remote or challenging environments.How Drones Are Controlled?
Drones are controlled using a combination of manual inputs from the operator and automated systems that ensure stable flight. Here’s a breakdown of how drone applications are controlled:
Remote Control
Operators use remote controllers or mobile apps to guide drones manually. They can adjust altitude, direction, and camera angles in real-time. UAV applications offer complete control, making aerial data collection easier, especially for photography and inspection tasks.
Autonomous Flight with AI
Some UAVs utilize AI to fly autonomous, pre-programmed routes. They collect data without any human input on the mission. Autonomous drones are perfect for repetitive tasks like herd and crop monitoring.
Key Sectors Utilizing Drone Applications
Drone applications offer tailored solutions to meet industry-specific needs. They improve workflow, reduce risk, and help teams achieve more in less time.The Application of Drones in Agriculture
Crop Monitoring and Health Analysis
Using the application of UAVs, farmers can evaluate plant health, identify any disease early enough, and make precise treatment decisions. Drones fly quickly over large areas in the field, giving a clear aerial view of crops. GPS-enabled drones help scan large farms with precision, providing real-time crop data.Precision Spraying and Seeding
Drones apply fertilizers and seeds only where needed, reducing waste and preserving resources. These targeted operations improve productivity while increasing crop yields.Livestock Tracking
Drones help monitor livestock location and behavior without disturbing the animals. Payload capacity allows drones to carry thermal cameras to monitor health and movement.Drone Applications in Construction & Infrastructure
Site Surveying and Mapping
Drones capture highly detailed aerial images, allowing them to form two-dimensional and three-dimensional site mapping. Drones not only reduce labor costs but also significantly shorten these survey processes.Progress Tracking and Inspection
Teams use drone applications to document work progress and detect structural issues early. Drone reports help keep projects on schedule and budget.Drone Application in Safety Monitoring
Drones assess risk areas and improve worker safety by reducing exposure to dangerous zones during construction inspections. Flight endurance enables more extended observation over large or high-risk construction sites.The Application of Drones in Logistics and Delivery
Last-Mile Package Delivery
Drones deliver goods quickly to homes and businesses, especially in hard-to-reach areas. They reduce delivery times and lower transportation costs.Warehouse Inventory Management
Drones scan shelves and count inventory faster than manual methods. The application of drones in warehouse help reduce errors and improve stock control.Route Optimization
Drones test delivery paths to find the fastest and safest routes. They use autonomous navigation to plan and adjust routes on the fly.Drone Applications in Public Safety and Security
Search and Rescue Operations
Drones locate missing persons faster in rough terrain or disaster zones. Real-time monitoring helps teams respond quickly and effectively during emergencies.Surveillance and Crime Monitoring
Police forces use drone applications to keep an eye on crowds or to keep an eye on suspicious activity, supported by application performance monitoring (APM) tools to ensure systems and real-time data remain reliable and operational. They serve as undercover support and do not put an officer at any risk.Firefighting Support
Drones locate hotspots and monitor fire movement to support firefighting crews. Thermal sensors help identify danger zones before crews enter.Traffic Management
Traffic drones monitor road conditions, detect accidents, and support real-time response. They help reduce congestion and improve public safety during peak hours or emergencies.Environmental and Wildlife Monitoring
Deforestation Tracking
Drones track illegal logging and forest health over time, gathering visual proof to support conservation efforts and policy changes.Wildlife Population Surveys
Researchers use drones to count animals without disturbing natural habitats. Aerial views give accurate population data for conservation planning.Natural Disaster Assessment
After storms or earthquakes, drones assess damage and guide relief efforts. Disaster assessment with drones helps speed up aid and reduce further risk.Media and Entertainment
Aerial Photography and Videography
Drones capture breathtaking views that were once expensive or impossible to film. They’re now widely used in journalism, travel, and sports content.Live Event Coverage
Event organizers use drones to capture sweeping views of concerts, festivals, and sports games, enhancing the audience experience with dynamic footage.Film Production Shots
Directors are using drones to capture cinematic viewpoints and fluid tracking views. Drones reduce the need for large camera rigs and helicopters.Advantages of Drone Applications in Industries
By guaranteeing improved drone efficiency, enterprises may reduce expenses and increase safety. Drone applications automate flight planning, mission execution, and data collection, streamlining workflows. Drones simplify complex tasks, allowing industry professionals to make better and wiser decisions in less time.
Cost Savings
Drones help save money by minimizing the use of equipment and reducing manual labor in inspection and surveillance. The application of drones also reduces the need for scaffolding, manual inspections, or even helicopters. As drones become faster and safer, these savings gradually reduce industries’ operating costs.
Better Data and Decision-Making
Drones isolate high-quality images, thermal scans, and 3D maps momentarily. Professionals rely on these data to guide their actions and make informed decisions. Data processing and analytics tools convert raw data into something valuable.
Enhanced Safety
UAVs reduce the need to place workers in dangerous environments, as public safety drones can traverse steep structures, hazardous zones, or unstable terrains while keeping a safe distance. Organizations follow strict safety protocols to ensure both UAV and human safety during missions.
Scalability and Versatility
Businesses can deploy a single drone or scale to a whole fleet. A drone’s flexibility supports various tasks across different locations and industries.
Regulatory Awareness
Modern drone programs emphasize proper use and legal compliance. Teams must understand airspace rules, privacy laws, and operating restrictions. Regulatory compliance ensures drones are used responsibly and within legal boundaries.
Challenges and Regulations in Drone Applications
Drones offer many advantages, but industries must deal with technical challenges, legal problems, and operational obstacles. Understanding the limitations will help ensure the safe and effective use of drone applications.
Airspace Restrictions and Legal Boundaries
Drones must follow local and national laws when flying in shared airspace. Operators need proper licenses, permissions, and insurance before commercial flights. Failure to follow regulations can lead to penalties and mission delays.
Managing Drone Fleet Operations
Drone applications for coordinating multiple drones require planning, communication, and oversight. Drone fleet operations demand centralized control, scheduling, and monitoring for efficiency and safety. Fleet managers use software to assign tasks and prevent overlap or collisions.
Technology Limitations and Compatibility
Not all drones work with every software or device. Compatibility issues may arise between hardware components and operating platforms. Sensor integration must be seamless to ensure reliable data collection and analysis.
Wireless Communication and Signal Interference
Drones rely on stable connections for real-time control and feedback. Wireless communication problems, like signal loss or interference, can disrupt missions. Strong signals and backup systems help prevent accidents or lost data.
Privacy and Ethical Concerns
Drone cameras can record sensitive areas or private property. Operators must respect privacy and follow ethical guidelines when capturing images or data. Transparency and trust are essential when working in public or residential spaces.
Environmental and Weather Constraints
Rain, wind, or extreme temperatures may affect drone performance. Bad weather can reduce battery life, flight time, and image quality. Operators must monitor forecasts to avoid mission failures or equipment damage.
The Future of Drone Applications Drone
The application of drones now includes automated scheduling, fleet coordination, and industry-specific workflows. Well-planned deployments improve results and reduce waste. As drone technology improves, tasks become faster, easier, and more consistent.
- Better battery life and AI-based navigation enhance operational efficiency.
- Real-time decision support helps streamline complex missions.
- Drones continue to replace expensive, labor-intensive methods across industries.
Drone applications reduce the need for equipment and human risk. Their greater cost-effectiveness makes them a wise long-term investment for small and large businesses. Drones also support environmental goals by reducing carbon emissions and resource use.
Drones help monitor ecosystems, protect wildlife, and track land use. Their low-footprint operations minimize the environmental impact of surveying and data collection.
Ready to Elevate Your Industry with ZenaDrone 1000?
As drones continue to revolutionize industries, the ZenaDrone 1000 stands at the forefront of innovation, offering unmatched efficiency and versatility across various sectors. Whether you’re in agriculture, logistics, or film production, this cutting-edge drone application is designed to elevate your operations.
Ready to experience the future of drone technology? Explore the ZenaTech’s drone application and see how it can transform your industry today!